Dark Matter Could Be Annihilating Inside White Dwarfs
Updated: 2023-09-29 17:00:00
 Skip to content Universe Today Space and astronomy news Menu Videos Newsletter Podcast Contact Us Support Us Log in The white dwarf Sirius B compared to Earth . Credit : ESA and NASA Posted on September 29, 2023 September 29, 2023 by Brian Koberlein Dark Matter Could Be Annihilating Inside White Dwarfs As the search for dark matter particles continues to yield nothing , astronomers continue to look at ways these elusive particles might be found . One general method is to look for evidence of dark matter particle decay . Although dark matter doesn’t interact strongly with regular matter , some dark matter models predict that dark matter particles can interact with each other , causing them to decay into regular particles There have been several searches for this effect , but there’s no
Skip to content Universe Today Space and astronomy news Menu Videos Newsletter Podcast Contact Us Support Us Log in The white dwarf Sirius B compared to Earth . Credit : ESA and NASA Posted on September 29, 2023 September 29, 2023 by Brian Koberlein Dark Matter Could Be Annihilating Inside White Dwarfs As the search for dark matter particles continues to yield nothing , astronomers continue to look at ways these elusive particles might be found . One general method is to look for evidence of dark matter particle decay . Although dark matter doesn’t interact strongly with regular matter , some dark matter models predict that dark matter particles can interact with each other , causing them to decay into regular particles There have been several searches for this effect , but there’s no
 A hypertriton is a tritium nucleus in which a neutron is replaced by a so-called Lambda hyperon. This type of hypernucleus was first discovered in the 1950s has since been the key focus of numerous studies.
A hypertriton is a tritium nucleus in which a neutron is replaced by a so-called Lambda hyperon. This type of hypernucleus was first discovered in the 1950s has since been the key focus of numerous studies.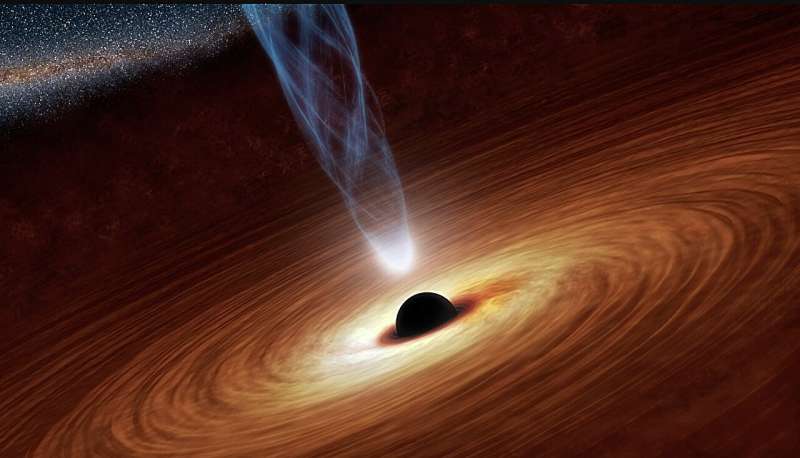 Black holes are regions in space characterized by extremely strong gravity, which prevents all matter and electromagnetic waves from escaping it. These fascinating cosmic bodies have been the focus of countless research studies, yet their intricate physical nuances are yet to be fully uncovered.
Black holes are regions in space characterized by extremely strong gravity, which prevents all matter and electromagnetic waves from escaping it. These fascinating cosmic bodies have been the focus of countless research studies, yet their intricate physical nuances are yet to be fully uncovered. Astronomers say they have spotted evidence of stars fuelled by the annihilation of dark matter particles. If true, it could solve the cosmic mystery of how supermassive black holes appeared so early
Astronomers say they have spotted evidence of stars fuelled by the annihilation of dark matter particles. If true, it could solve the cosmic mystery of how supermassive black holes appeared so early